Shifting away from conventional lithium-ion battery electrode production methods, which typically involve environmentally harmful wet coating processes using toxic solvents like N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), researchers have introduced an innovative dry press-coating technique. This new approach is not only more environmentally friendly but also enhances the performance and manufacturing efficiency of batteries. Traditionally, the process of drying and recycling NMP significantly increases production costs, as it represents a large fraction of the overall cost of battery manufacturing.
A study by Minje R. et.al. explored a 'dry press-coating' method that employs a composite of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) in dry powder form, along with etched aluminum (Al) foil serving as the current collector. This technique eliminates the need for harmful solvents and results in electrodes that are mechanically stronger and perform better than those produced by traditional slurry coating methods. The NCM712 electrodes created with this technique demonstrate impressive specific and volumetric energy densities, indicating the potential of this method for producing high-performance energy storage systems.
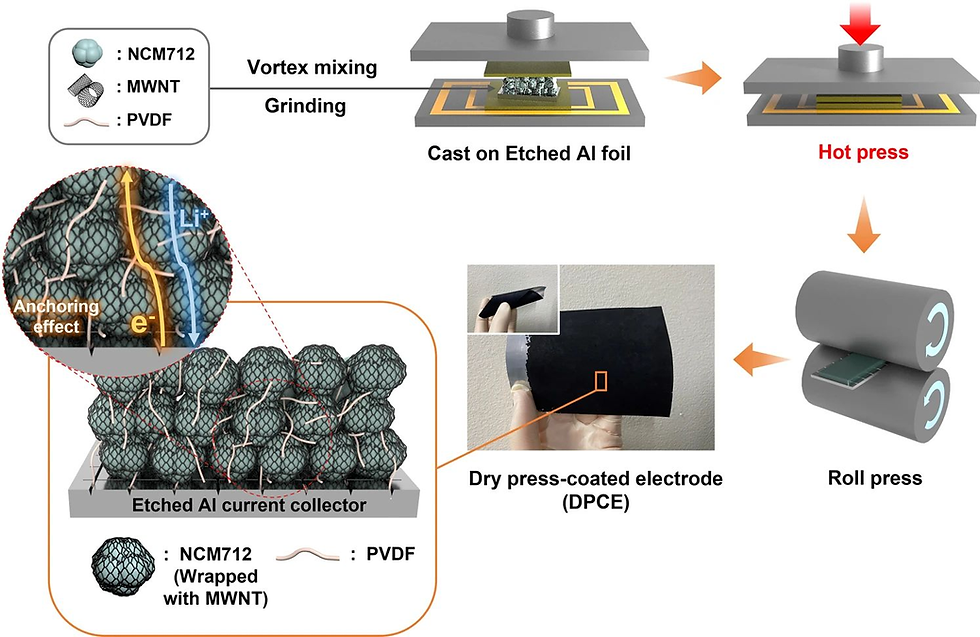
The process starts with the vortex mixing of NCM712, MWNT, and PVDF, which are then ground into a fine powder. This mixture is cast onto an etched aluminum foil, which acts as the current collector, and is then hot pressed to create a uniform coating. A roll press step ensures the electrode's density and mechanical strength, essential for its use in battery cells. The resulting dry press-coated electrode (DPCE) is flexible and features a complex network of active materials and carbon nanotubes, which ensures both mechanical integrity and electrical conductivity.
By removing the need for drying and recycling NMP, the dry press-coating method significantly lowers both the operating costs and energy consumption of battery production. Additionally, it enables the creation of electrodes with high mass loadings, which is crucial for improving the energy density and efficiency of batteries.
The introduction of the dry press-coating technique marks a significant advancement in lithium-ion battery technology, addressing environmental and health concerns linked to traditional electrode production methods. It also brings notable improvements in battery performance and manufacturing efficiency. While the dry press-coating method in general faces challenges such as scaling up for mass production and ensuring consistency in electrode quality, ongoing research and development like this hold the promise of overcoming these obstacles.